Student Activities for Global Warming
Essential Questions for the Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
- What is the greenhouse effect?
- What is global warming?
- What causes global warming?
- How can we reduce global warming?
- Why is there so much controversy over global warming?
Global Warming and Climate Change
The amount of carbon dioxide in our atmosphere has been increasing since the industrial revolution. From the late 18th century, the rise of machines powered by burning fossils fuels led to amazing growth in manufacturing. These machines were mostly powered by burning large amounts of coal. Coal is made of mainly carbon and when burned, produces carbon dioxide. The word equation for combustion is fuel + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water.
Although now mills and factories are mainly powered using electricity, humans around the world still rely on fossil fuels, such as crude oil and coal, as some of our main energy resources. In fact, some means of generating electricity involve the burning of fossil fuels. Deforestation also has an effect on the amount of carbon dioxide is deforestation. Deforestation is the act of clearing trees away from an area and not replacing more trees. Photosynthesis is a process that removes carbon from the atmosphere. It is a chemical reaction that plants use to make their own food. If many trees are destroyed and not replaced, there are fewer plants to remove carbon from the air. To find out more about how carbon moves to and from the atmosphere and living things, check out our carbon cycle lesson plans.
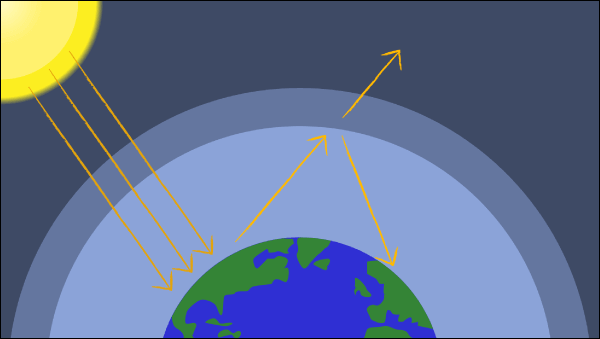
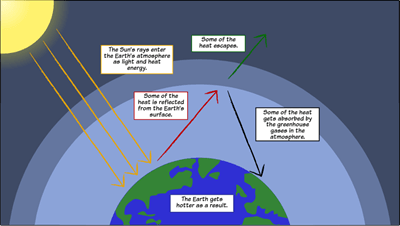
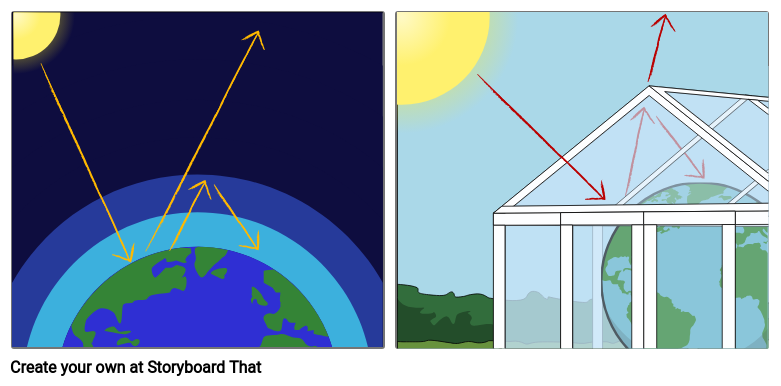
Scientists have noted that the average temperatures on Earth have been increasing over time. They believe one contributing factor of this is the greenhouse effect. This effect is caused by the buildup of greenhouse gases, such as methane, water vapor, and carbon dioxide. Methane can come from decomposing organic material; a man-made source of methane is farming. Carbon dioxide can come from combustion, as in a car engine. Atmospheric water vapor can come from evaporating seas and lakes, but also as a byproduct of combustion. The Earth absorbs radiation of all wavelengths from the Sun and some of this radiation causes the Earth to warm up. This heat is radiated away from the Earth as infrared. The greenhouse gases absorb and trap this energy, causing the atmosphere to warm up. This is the same way a greenhouse works. The glass lets the radiation through into the greenhouse, but it won’t let the heat leave.
Although the link between the rising levels of greenhouse gases and increase in global temperatures is well agreed upon in the scientific community, the cause of the increase of greenhouse gases is not. There are some scientists that believe that this change in the composition of the atmosphere is natural. They believe that the composition of the atmosphere naturally varies in cycles, with times when the levels of greenhouses gases is high and other times when it is low. The vast majority of the scientific population however, believe that the increase in global temperatures is due to human activity.
However, an increase in global temperatures will lead to climate change, which is a change in the average weather experience in an area over a few decades. This could lead to more droughts in the summer and storms with extreme snow in the winter. Change in climates across the world could have devastating effects on landscape, animal life, and even human life. Potential effects can include different migration patterns for some animals or crops not growing as well in areas of the world were they used to be abundant. Some areas may experience more extreme weather as the global temperatures increase. The increase in temperature also will affect the amount of polar ice. As this ice melts and with the thermal expansion of the oceans, the sea level rises. This can be particularly dangerous for some low-lying island nations such as the Maldives, a country which is already susceptible to coastal flooding. Animal habitats have also been affected by the change in global temperatures. The Adélie penguins, which alongside Emperor penguins are the only true antarctic penguins, may become endangered as the amount of space they can inhabit in Antarctica is shrinking.
There are many ways that people are working towards reducing our carbon footprint. Using less electrical energy in our homes can reduce the amount of fossil fuels burned in power stations. Small acts like switching off lights when they are not in use or turning your heating down by a few degrees can reduce the amount of carbon dioxide released in the atmosphere. Many engineers and companies are working around the world to produce practical electric cars that would allow us to reduce our need of crude oil and to produce less carbon dioxide.
There are many different renewable energy resources that are set to replace current fossil-fuel power plants. Engineers are working to make these resource more efficient and more affordable. To find out more about energy resources check out the energy resources lesson plans.
How Tos about Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
Engage students with a hands-on carbon footprint tracking project
Assign each student or group a simple log to record daily activities that use energy (e.g., lights, electronics, transportation). Tracking these behaviors helps students see how everyday choices impact greenhouse gas emissions.
Guide students to research the carbon impacts of common school activities
Encourage students to investigate how classroom routines—such as printing worksheets or commuting—contribute to carbon dioxide emissions. This raises awareness and sparks discussion on reducing energy use at school.
Discuss simple ways students and families can reduce their carbon footprint
Lead a class brainstorm to list practical changes like turning off unused lights, recycling, walking instead of driving, and conserving water. Highlight how small actions add up to make a big difference.
Create a classroom pledge for climate-friendly habits
Collaborate with students to write a pledge outlining eco-friendly commitments, such as limiting waste or supporting renewable energy. Display the pledge to build accountability and ongoing motivation.
Reflect on project results and celebrate positive changes
Review carbon footprint logs and class pledges together. Celebrate improvements and discuss new goals, reinforcing students' sense of agency in fighting global warming.
Frequently Asked Questions about Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
What is the greenhouse effect and how does it contribute to global warming?
The greenhouse effect is the process where gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor trap heat in Earth's atmosphere, much like glass in a greenhouse. This trapped heat leads to global warming by raising average global temperatures.
What activities can students do to learn about global warming in the classroom?
Students can explore hands-on activities such as charting greenhouse gas sources, modeling the greenhouse effect, researching climate change impacts, and discussing ways to reduce carbon footprints to better understand global warming.
What are the main causes of global warming?
Global warming is mainly caused by increased greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels, methane from farming, and deforestation, which reduces carbon removal from the atmosphere.
How can teachers help students take action against climate change?
Teachers can encourage students to reduce energy use, choose renewable resources, participate in school sustainability projects, and learn about the impact of everyday choices on the environment.
What are some examples of renewable energy resources for reducing carbon emissions?
Examples of renewable energy resources include solar power, wind energy, hydroelectric power, and geothermal energy. These alternatives help reduce carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
- • TheDigitalArtist • License Free for Commercial Use / No Attribution Required (https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0)
- Burn • Hellcanwait • License Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
- Carbon dioxide molymod • activescience • License Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
- Coal • oatsy40 • License Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
- Fire • hans.emtenas • License Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
- Gas stove flame • Ervins Strauhmanis • License Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
- Hess Gas Station - Near Intrepid Museum • m01229 • License Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
- smoking chimney • quapan • License Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
- The Hubble eXtreme Deep Field • Hubble Space Telescope / ESA • License Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
© 2026 - Clever Prototypes, LLC - All rights reserved.
StoryboardThat is a trademark of Clever Prototypes, LLC, and Registered in U.S. Patent and Trademark Office