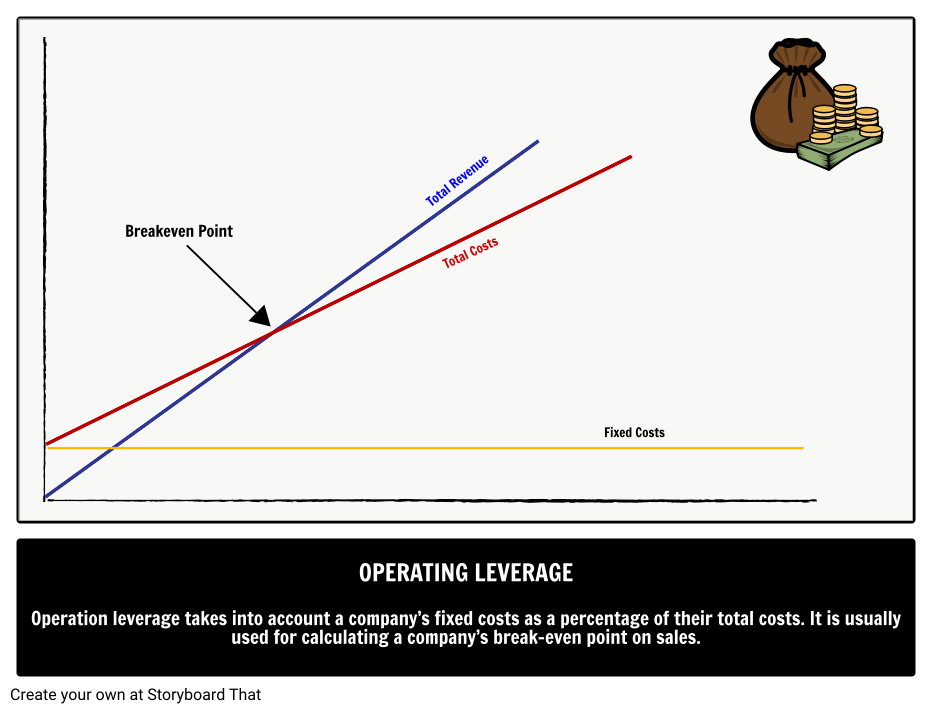
Operation leverage takes into account a company’s fixed costs as a percentage of their total costs. It is usually used for calculating a company’s break-even point on sales
The formula for calculating operating leverage is Contribution Margin/ Net Operating Income. Companies tend to fall into two categories of operating leverage:
- High Operating Leverage – this is a company with high fixed cost relative to their total costs. A company with high operating leverage has low variable costs, so the contribution margin on each unit sold yields relatively high profit for the company. This high profit is then used to pay off the high fixed costs, which means they need a high volume and steady stream of sales to stay profitable. An example of this is a software company. Selling 10 subscriptions vs. 1000 subscriptions has almost no impact on variable costs, but in either scenario the company will still have to pay expensive developer salaries.
- Low Operating Leverage – this is a company where the fixed costs are relatively low, and most of their expenses come from variable costs. A company like this has a smaller contribution margin, but also needs to make fewer volume of sales to be profitable, since they have low fixed costs. An example of a company with a low operating leverage could be an electrician company. When a client needs work, they need to go out and buy supplies to get the job done. The cost of supplies takes a chunk out of the total profit, but the company doesn’t have to worry about a nice big expensive office space in their fixed costs.
How Tos about Operating Leverage: Definition and Examples
Introduce operating leverage with a relatable classroom analogy
Start by comparing operating leverage to a lemonade stand with fixed costs. Explain that just like paying for a table and supplies before selling lemonade, businesses have costs they must cover before making profits. This analogy helps students connect complex financial concepts to familiar experiences.
Create an interactive activity to demonstrate fixed vs. variable costs
Organize a classroom simulation where students list expenses for running a pretend business. Assign some costs as fixed (like rent) and others as variable (like ingredients). Let teams calculate how profits change as they sell more or fewer products. This hands-on approach makes the concept memorable and practical.
Use visual aids to illustrate the impact of operating leverage
Draw simple graphs on the board showing revenue, fixed costs, and variable costs as sales increase. Highlight how profits grow faster once fixed costs are covered due to operating leverage. Visuals help students see the relationship between costs and profit clearly.
Integrate math problems to reinforce understanding
Give students basic math problems to calculate profit at different sales levels, considering both fixed and variable costs. Challenge them to find the break-even point and discuss how increasing sales affects profit. This builds math skills while reinforcing financial concepts.
Encourage students to present their findings to the class
Invite groups to share what they learned about operating leverage and how it impacts business decisions. Facilitate a discussion on real-world examples, like restaurants or movie theaters. Student presentations boost confidence and deepen understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions about Operating Leverage: Definition and Examples
What is operating leverage in business?
Operating leverage is a measure of how a company's fixed and variable costs affect its profits as sales change. High operating leverage means small sales increases can lead to big profit jumps.
How does operating leverage impact a company's profits?
Companies with high operating leverage experience larger profit increases when sales rise, because most costs stay the same. However, profits can drop quickly if sales fall.
Why is operating leverage important for teachers and students to understand?
Understanding operating leverage helps students see how businesses make financial decisions and manage risk, which is key for economics, business, and math lessons.
What is the difference between operating leverage and financial leverage?
Operating leverage deals with the impact of fixed costs on profits, while financial leverage relates to how debt (borrowed money) affects company earnings.
Can you give an example of operating leverage in real life?
A factory with high fixed costs but low variable costs shows operating leverage. If it sells more products, profits grow quickly because most expenses are already paid.
© 2026 - Clever Prototypes, LLC - All rights reserved.
StoryboardThat is a trademark of Clever Prototypes, LLC, and Registered in U.S. Patent and Trademark Office